Setup ECMP on Mikrotik router
ECMP
ECMP (Equal-Cost Multi-Path) is a routing technique used in networking where multiple paths to a destination have the same cost. ECMP allows routers to load-balance traffic across these equal-cost paths, improving bandwidth utilization and redundancy.
Benefits of ECMP
- Increased Bandwidth and Throughput: ECMP allows for the aggregation of bandwidth across multiple network links, effectively multiplying the capacity and enabling higher throughput for data traffic.
- Load Balancing: Traffic is distributed across multiple paths, which helps to avoid congestion and optimizes the usage of network resources. This distribution can help preven any single path from becoming a bottleneck.
- Redundancy: By having multiple paths available, ECMP enhances the network’s ability to remain operational even if one or more paths fail.
- Scalability: As network demands grow, ECMP can handle increased traffic by simply adding more paths without needing significant changes to the network’s core architecture.
In a network with multiple paths to a destination, without ECMP, only one path is selected, leaving the other paths unused. This leads to all traffic being routed through a single path, causing bottlenecks and offering no redundancy if the path fails. After applying ECMP, traffic is evenly distributed across all equal-cost paths, reducing congestion and ensuring that if one path fails, the other paths can still carry the traffic, providing both better performance and fault tolerance.
How ECMP works
When traffic arrives at the router, the router applies a hashing algorithm to various fields in the packet (such as source/destination IP, source/destination port, etc.) to determine which of the available equal-cost paths to use. This ensures that packets belonging to the same flow (e.g., a TCP session) always take the same path to avoid out-of-order delivery, while different flows may take different paths. This load-balancing mechanism enhances bandwidth utilization and provides redundancy, ensuring that the network can continue operating efficiently even if one path fails.
ECMP typically uses a hashing algorithm to determine the path for each flow, but other algorithms like round-robin, per-packet load balancing, or weighted round-robin can also be used to distribute traffic across multiple paths, depending on the network configuration. These algorithms offer different methods for balancing the load and managing traffic flows in the network.
Setup ECMP
1. Update IP hash policy
Update the IP hash policy settings from l3 (layer-3 hashing of src IP, dst IP) to l4 (layer-3 hashing of src IP, dst IP). This allows for more efficient load balancing across multiple paths.
1 2 3 4 | |
Why L4? Layer 4 hashing provides better distribution by including port information, resulting in more effective load balancing across connections.
2. Adjust Route Distances in the main Routing Table
Set incremental distances for default routes in the main routing table.
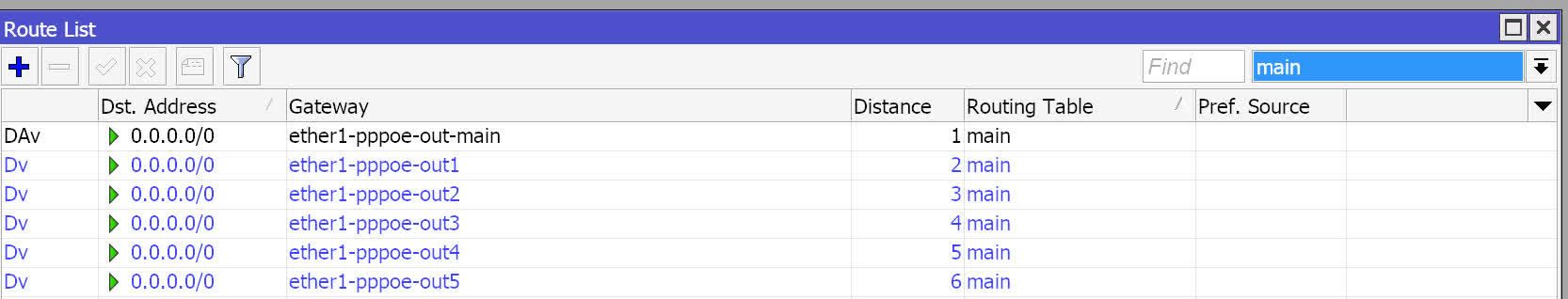
If multiple routes in the main table have the same distance, the router will treat them as ECMP routes, and the + sign will appear, indicating that ECMP is active.
By setting incremental distances, only the route with the lowest distance is used, while the others act as failover routes.
Why disable ECMP in main table?
Certain traffic requires a consistent outbound path and source IP. ECMP in the main table could cause frequent path/IP changes, breaking:
- Banking websites (IP-based fraud detection)
- VPN connections (session persistence)
- IP-sensitive or session-based applications
[!NOTE] Traffic requiring stable routing is directed to the
maintable via routing rules, while general traffic uses theecmptable for load balancing.
3. Create a new routing table for ECMP.
1 2 | |
4. Add Routes to the ECMP Routing Table
Add default routes with equal distances to enable ECMP:
1 2 3 4 5 6 | |
5. Traffic Steering (Routing Rules)
Routing rules determine which traffic uses which table. Order matters - rules are processed top-to-bottom. Add a base rule to ensure all traffic is processed (must be in the top)
Rule 1: The Local Bypass
This rule ensures that internal traffic (LAN-to-LAN, LAN-to-Router, or VPNs) stays in the main table. Without it, your router may try to send a local print job or a file transfer out to the internet via your WAN gateways (ecmp).
1 2 | |
Understanding min-prefix=0 (The "Suppression" Secret)
In MikroTik routing rules, the min-prefix parameter acts as a result filter. It does not decide which route to look for, but rather decides whether to accept or ignore the route the router found.
The Rule of Thumb: Look in the table. If the Prefix Length (the subnet mask) of the best matching route is <= the min-prefix value, the router will suppress (ignore) that result and move to the next routing rule.
| min-prefix | The Router says... |
|---|---|
| 0 | Ignore only the 0.0.0.0/0. Accept everything else (local LAN /24, VPNs, etc.). |
| 24 | Ignore any route with a mask <= 24 (like /0, /16, /23, /24). Only accept very specific routes like /25 or /32 |
Scenario A: A user at 192.168.10.5 wants to view a camera at 192.168.20.100
- Router Action: It looks in the main table for
192.168.20.100 - Best Match Found:
192.168.20.0/24 - Prefix Length:
24 - Logic Check: Is
24 <= 0? No - Result: The router Accepts the route from the main table. The traffic is routed internally between VLANs. It is not sent to the ECMP load-balancer.
Scenario B: The user at 192.168.10.5 goes to netflix.com (45.57.94.1)
- Router Action: It looks in the main table for
45.57.94.1 - Best Match Found: None of the specific routes match, so it hits the Default Route
0.0.0.0/0 - Prefix Length:
0 - Logic Check: Is 0 <= 0? Yes
- Result: The router Suppresses (ignores) this result. Because it "rejected" the internet route in the main table, it moves down to your next Routing Rule
Rule 2: The VIP Exception
Forces specific sensitive devices (like a work laptop for banking) to bypass load balancing and use the primary WAN defined in the main table.
1 2 | |
[!NOTE]
My wife works remotely and connects to her company VPN, which uses strict IP-based session tracking. If ECMP shifts her traffic from WAN1 to WAN2, her public IP address changes instantly. To the company’s security system, this can look like a session hijacking attempt and may trigger an automatic security block on her account. This rule ensures her laptop maintains a persistent, single-IP identity on the primary WAN.
Rule 3: The ECMP Catch-ALL
Any traffic that wasn't local (skipped Rule 1) and wasn't a VIP (skipped Rule 2) is caught here and forced into the ecmp table to be load-balanced across all WANs
1 2 | |